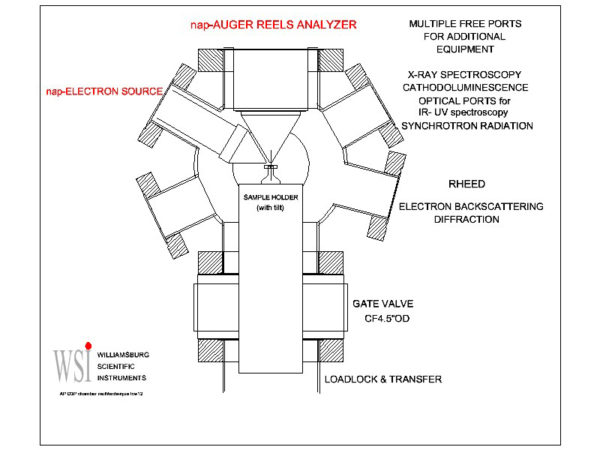
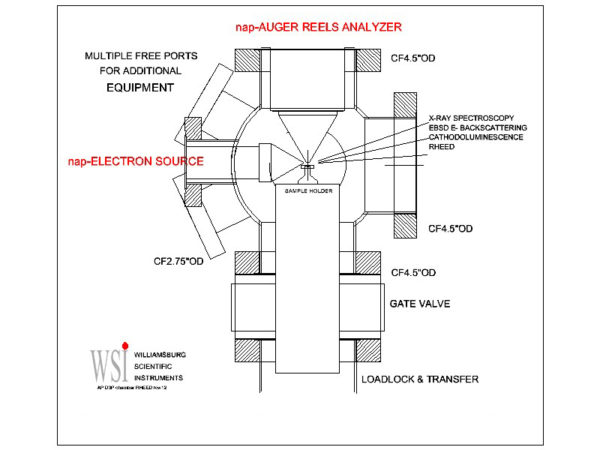
Auger Electron Spectroscopy (AES) at Near Ambient Pressure
A new energy spectrometer was developed to perform in-situ and experimendo surface analysis in deposition chambers allowing the elemental surface composition to be followed during growth. The analyzer design is modified to include powerful differential pumping in order to maintain a sufficiently low vacuum pressure along the path of the analyzed electrons. The operating vacuum pressure range is mainly determined by the efficiency of the pumping and the nature of the NAP gases. Several options are available to suit the experimental environment conditions. From single differential pumping (DP-1) to triple differential pumping (DP-3) Auger spectroscopy can be performed from UHV up into the 100 mTorr range.
| Model | nap-AP-DP1 | nap-AP-DP2 | nap-AP-DP3 |
| Pumping stages | 1 | 2 | 3 |
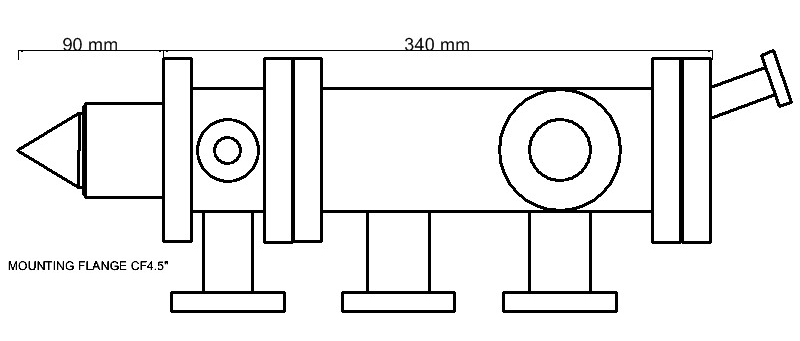
| Mounting flange (inch OD) | CF 2.75 CF 4.5 |
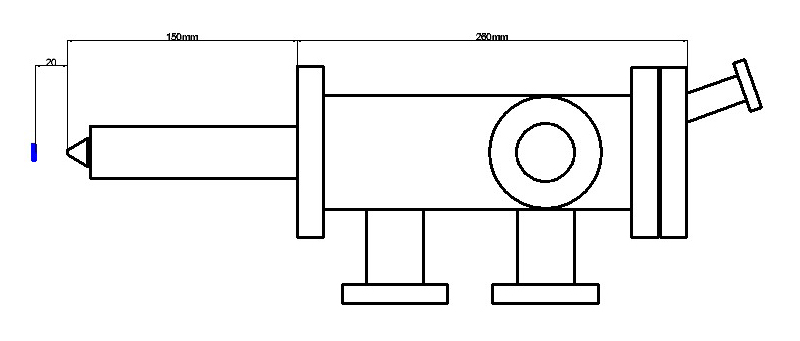
CF 4.5 CF 6 |
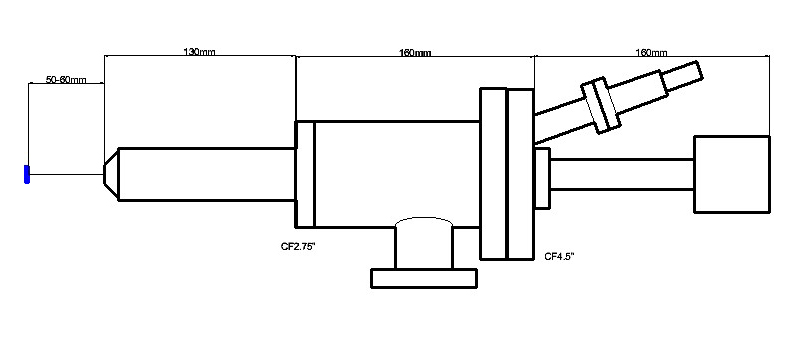
CF 4.5 CF 6 |
| Min. pressure | UHV | UHV | UHV |
| Max. operando pressure (N2) | 10 mTorr | 30 mTorr | >100 mTorr |
| Working distance (mm) | 50-60 | 10-20 | 2-4 |
All information is subject to modification at any time and is not part of the technical specifications.
Differential Pumping Options
All electron sources are available with single (DP1), double (DP2) or triple (DP3) pumping capabilities in cases where the operating pressure is less than indicated in the above table.
NAP-Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy (REELS)
Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy (EELS) is a powerful addition to AES because it delivers information closely related to the chemical state of the sample. A fraction of the primary electron is reflected (or backscattered) from the surface and the energy distribution near the elastic peak is measured. It shows discrete peaks and structures corresponding to energy losses (Characteristic Energy Losses CEL). These are classified as plasmon excitations (volume and surface plasmons are separated), band transitions and ionization losses corresponding to core level excitations. Hence the electrons are backscattered from the surface and the energy losses are measured in reflection, this technique is often referred to as REELS.
The nap-AP has an electronically adjustable high energy resolution that can be set to values suitable for REELS analysis. As the energy analyzer operates in an energy range up to 2,000 eV, the beam energy has to be set in this low energy range, meaning that the scattering effects are more pronounced and the maximum operando pressure is correspondingly lower.
REELS data can be obtained from any nap-AP system equipped with a nap-electron source able to operate at low energy.